The reconstruction rhinoplasty is a maximum complexity level ordeal above the revision rhinoplasty or secondary rhinoplasty noses and joining techniques of major reconstructive plastic surgery, aggravated due to some very specific injuries, damage to tissues, absence of anatomical elements, excessive resection or trimming of some essential parts, devascularization, massive fibrosis, necrosis, calcifications, loss, shrinkage or contraction of the outer skin cover or the inner airway lining, missing absence or wrong indication, graduation, calibration or execution of techniques applied, wasted or damaged grafting donor sites, poor aesthetic judgement, loss of critical support pillars, unsuitable balance, unforeseeable intraoperative findings and other factors, requiring meticulous debridement and cleansing of unstable, fibrotic and necrotic tissue to indentify viable structures and remove those not, perform a final diagnosis of situation to plan the definitive technical repair strategy and achieve a healthy and well vascularized recipient bed for grafting, plus massive requirements of additional structure supply with large, thick and multiple cartilage grafting often involving the rib as donor site, fascia grafting and others, and eventually requiring the addition of fresh cutaneous or mucosa cover with grafts or flaps; those patients with mixed ethnic features plus post-traumatic and post-surgical sequels may present technical challenges belonging all those groups; the deeper and more extensive the damages of the inner structures, outer cover and airway lining of the nose the higher the complexity, the more demanding in invention and creativity, the lesser the chances of complete repair, the longer the surgical time and the more escalated the costs are bound to be.
Some of the most common techniques applied in the reconstruction rhinoplasty are cartilage grafting harvested from nasal septum, ear's concha bowl or rib cartilage, harvesting of deep or superficial temporalis fascia grafting, tip domal plication or suturing, plasties of tip domes, alternate incomplete domal transections, tip graft, Sheen's graft, shield graft, columellar strut or tutor graft, lateral cruras tutor or batten graft, lateral cruras exchange or crossed location, lateral cruras replacement graft, lateral cruras caudal extension graft, tongue in groove fixation of medial cruras, lateral and medial cruras plication or suturing, lateral and medial cruras length trimming for shortening or grafting for lengthening, lateral and medial cruras repositioning, medial cruras footplates plication or suturing, nostrils rim graft, middle vault spreader or spacer grafts, paramedian reduction of dorsal plateau or rhombus, septal lengthening graft, septal caudal extension grafts, dorsal onlay graft, supratip graft, radix graft, dorsal fascia graft and other custom grafting, alar base reduction, nostrils reduction, local, regional and distant grafts or flaps of skin and mucosa and other custom procedures.
Typical scenarios where a reconstruction rhinoplasty is performed are the short nose, long nose, poorly defined tip, short or underprojected tip, overprojected tip or Pinocchio's nose, bifid or cleft tip and columella, bulbous tip, boxy tip, asymmetric tip, buckled tip, tip irregularities, inverted or concave lateral cruras, over rotated or upturned tip, piggy nose, severely hooked or droopy tip, hanging columella or columellar exposure show, alar rim retraction, septal mucosa exposure show, sunken supratip, polly beak deformity or supratip prominence, tension nose, pinched middle vault, hourglass dorsum, high placed, missing, absent or incompetent osteotomies, open roof deformity, inverted V deformity, rhomboid or broad humpless dorsum, dorsal ridges, dorsal irregularities, low sunken dorsum or saddle nose deformity, low radix, high humpless dorsum, high radix, prominent alar flare, large nostrils, filmy and transparent nasal skin, skin damage, pinched or incompetent nasal valve, airway synechia, severe asymmetries, crookedness, non reduced fractures, shattered nasal bones, septal fracture, shortfall of skin or mucosa cover, missing nasal bones, oncological mutilations and others.
This nose job is normally carried out by means of the open rhinoplasty or external approach at the columella and also inside the nostrils, alar base and others, with optimal quality and well concealed scars, through which structure of the nose is modified as well as resized, grafting applied, plications or sutures performed and other maneuvers executed; additional well hidden scars behind the ear, within the hairy temple scalp, underneath the breast and others might be necessary as donor sites of any grafted material; should skin and mucosa flaps or grafts be required their donor sites will show explicit and unsightly scars.
Patients warning: only highly experienced surgeons who have underwent optimal training and have performed already a large number of closed and open approach structure and non structure rhinoplasties should execute high end rhinoplasty cases, should they feel capable and comfortable with the challenge.
READ LESS ABOUT RECONSTRUCTION RHINOPLASTY

 READ MORE ABOUT SURGERY SHIELD
READ MORE ABOUT SURGERY SHIELD

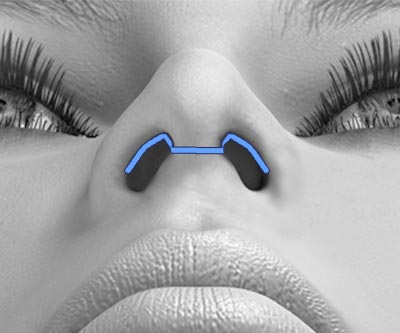
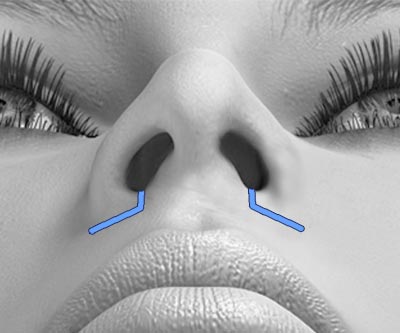
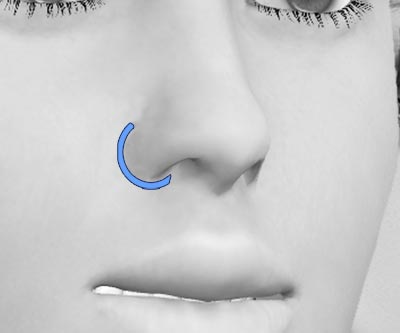
 READ MORE ABOUT BENEFITS OF THE COLLABORATIVE MODEL
READ MORE ABOUT BENEFITS OF THE COLLABORATIVE MODEL